IGCSE Biology 0610
1.3 Features of organisms
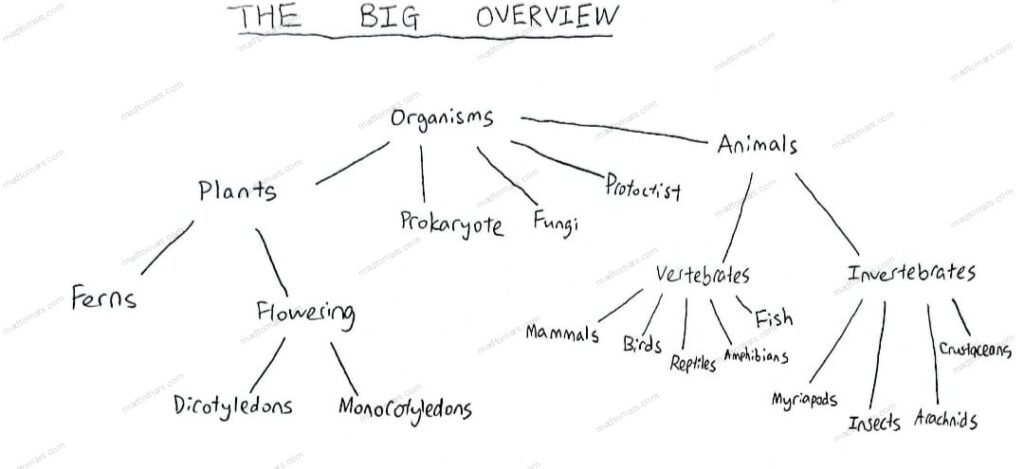
Kingdoms of Organisms and their Features
- The 5 kingdoms of organisms are: animal, plant, fungus, prokaryote, protoctist
Plants:
- Multicellular organisms
- Growth occurs in special places (eg. tips of roots and stems)
- Bodies are not compact
- Make their own food through photosynthesis
- Have cell walls, chloroplasts, large vacuoles
- No nervous system
- Cell walls are made of cellulose
Animals:
- Multicellular organisms
- Growth occurs throughout body
- Bodies are more compact than plants
- Cannot photosynthesise, obtain food by eating plants and/or animals
- No cell walls, chloroplasts, large vacuoles
- Have nervous systems which coordinate responses to stimuli
Fungi:
- Most are multicellular except yeast
- Some are microscopic, some are non-microscopic
- Cells have nucleus
- Have cell walls are that are made of chitin
- Reproduce by spores
Prokaryotes:
- Prokaryotes include bacteria
- Microscopic
- Simple cell structure
- Spherical or rod-shaped
- Cells have cell walls
- Some cells have slime capsules
- No nucleus
- Circular DNA in cytoplasm, some extra loops in plasmids
- Some have flagella to move through liquids
Protoctists:
- Do not belong in other four kingdoms
- Cells have nucleus
- Most are unicellular, some are multicellular
- Some protoctists can contain chlorophyll such as algae
Groups within the Animal Kingdom
- The animal kingdom can be divided into vertebrates and invertebrates
- Vertebrates have backbones and internal skeletons
- Invertebrates do not have backbones, but have external skeletons
- Vertebrates consist of: mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish
Mammals:
-humans, dogs, bats, dolphins..
- Have hair/fur
- Have external ears
- Females suckle young with milk with mammary glands
- Have lungs to breathe
- Internal fertilisation and development
- Homeothermic (maintain a constant internal temperature)
- Double circulatory system
Birds:
-hawks, eagles, sparrows, parrots..
- Have feathers and wings
- No teeth
- Breathe through lungs
- Internal fertilisation, external development by laying hard shelled eggs
- Homeothermic (maintain a constant internal temperature)
- Double circulatory system
Reptiles:
-crocodiles, lizards, snakes, turtles, tortoises..
- Have dry, scaly skin
- Internal fertilisation, external development by laying soft-shelled, leathery eggs
- Have lungs
Amphibians:
-frogs, toads, salamanders
- Have smooth, moist skin
- Live on land, breed in water
- External fertilisation – sperm and eggs released into water
- External devlopment
- Lay eggs that do not have shells
- Tadpoles breathe through gills
- Adults breathe through lungs on land, breathe through skin in water
Fish:
-tuna, herring, shark, catfish..
- Have fins to swim
- Breathe dissolved oxygen in water through gills
- Skin has wet scales
- Live in water permanently, though some can survive out of water for short periods
- Most have external fertilisation
- Lay eggs
- Single circulatory system
- Invertebrates consist of: myriapods, insects, arachnids, crustaceans
Myriapods:
-centipedes and millipedes
- Many segments on body
- Centipedes have one pair of legs on each segment
- Millipedes have two pairs of legs on each segment
Insects:
-ants, beetles, flies..
- Body divided into 3 segments, head, thorax, and abdomen
- Three pairs of legs on the thorax
- One pair of antennae
- Insects that can fly have 2 pairs of wings
- Have compound eyes
- Breathe through holes in thorax and abdomen called spiracles
Arachnids:
-spiders, scorpions, ticks..
- Body divided into 2 parts, cephalothorax and abdomen
- 4 pairs of legs
- No wings
- No antennae
- Several pairs of simple eyes
- Paralyse prey with poison fangs
Crustaceans:
-crabs, shrimps, woodlice..
- Body divided into 2 parts, cephalothorax and abdomen
- Have a chalky exoskeleton
- 2 pairs of antennae
- Have compound eyes
- 5-20 pairs of jointed legs
- Almost all live in water
- Breathe through gills
Groups within the Plant Kingdom
- The plant kingdom can be divided into ferns and flowering plants
- Flowering plants can be further divided into dicotyledons and monocotyledons
Ferns:
- Leaves have a waxy layer which reduces water loss
- Do not produce seeds
- Make and release microscopic spores instead
- Leaves are called fronds
Flowering plants:
- Reproduce by flowers which make seeds
- Seeds form in ovary
Dicotyledons - Broad leaves
- Leaf veins branch (reticulated)
- Two cotyledons (seed leaves) in a seed
- Petals in multiples of 4/5
Monocotyledons - Narrow leaves
- Parallel leaf veins
- One cotyledon (seed leaf) in a seed
- Petals in multiples of 3
Viruses
- Particles are made up of genetic material
- Surrounded by a protein coat
- No cells, therefore not classified in 5 kingdoms