IGCSE Biology 0610
2.1 Cell structure
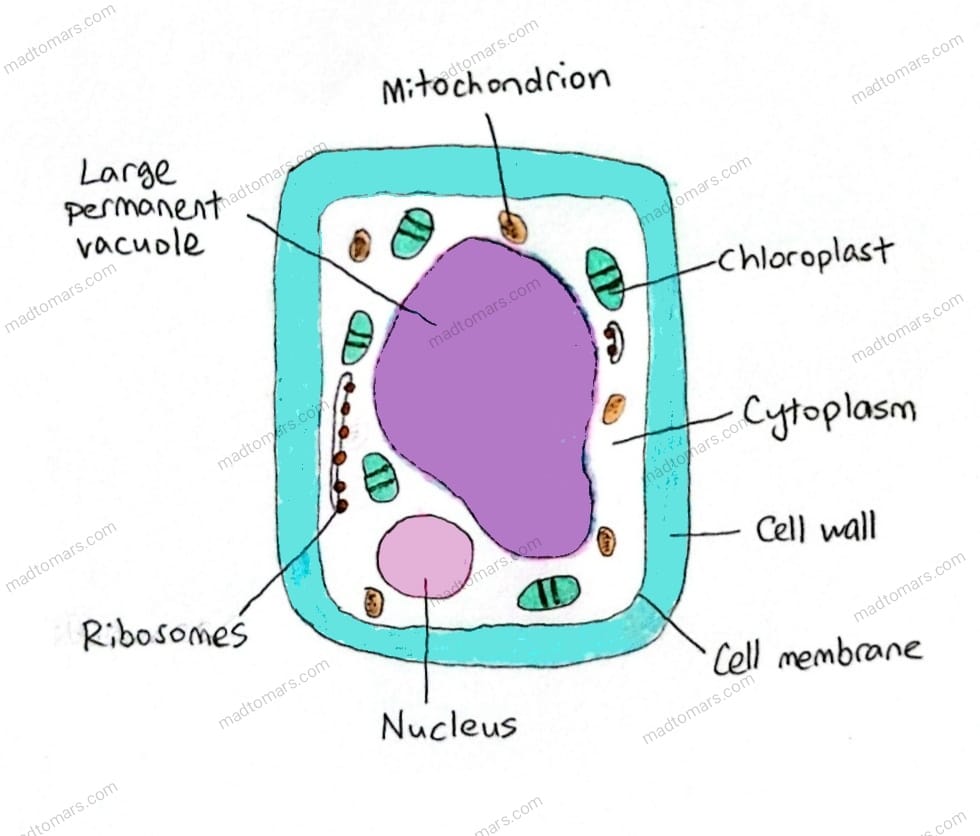

Comparing Plant and Animal Cell Structures
| Feature | Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
| Cell wall | Present | Absent |
| Cell membrane | Present and surrounded by cell wall | Present |
| Nucleus | Present | Present |
| Cytoplasm | Present | Present |
| Chloroplasts | Present in some cells | Absent |
| Ribosomes | Present | Present |
| Mitochondria | Present | Present |
| Vacuoles | Large permanent vacuole in cytoplasm containing cell sap | Small vacuoles in cytoplasm that do not contain cell sap |
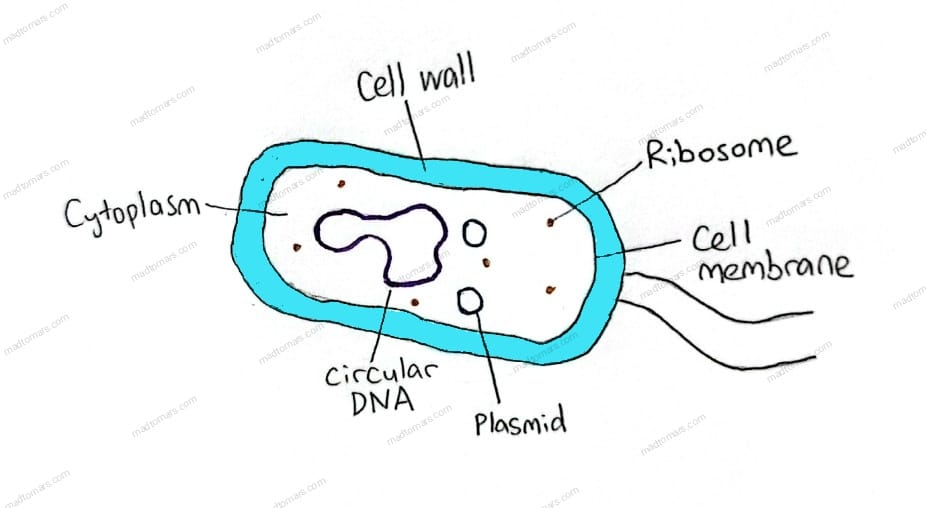
Bacterial Cell Structure
| Cell wall | Present |
| Cell membrane | Present |
| Cytoplasm | Present |
| Ribosomes | Smaller than those in eukaryotic cells, found in cytoplasm and NOT attached to rough endoplasmic reticulum |
| Circular DNA | Found in cytoplasm |
| Plasmids | Sometimes present, they are small rings of DNA that contain extra genes |
Prokaryotic cells = Do not have nucleus
Eukaryotic cells = Have nucleus
Functions of Cell Structures
| Cell wall | -Stops cells from bursting when filled with water -Gives shape to cells -Allows water and dissolved substances to pass through freely -Fully permeable |
| Cell membrane | -Forms a barrier between cell and surroundings -Keeps cell contents inside -Allows simple substances to pass through -Controls movement of other substances into or out of cell -Partially permeable |
| Nucleus | -Controls all activities in the cells -Controls how cells develop |
| Cytoplasm | -Place where many metabolic reactions occur |
| Chloroplasts | -Photosynthesis -Store starch |
| Ribosomes | -Synthesise proteins |
| Mitochondria | -Sites of aerobic respiration |
| Vacuoles | -Full of water to maintain shape and firmness of cell -Stores salts and sugars |
| Circular DNA | -Contains essential DNA |
| Plasmids | -Contains non-essential DNA |
- New cells are produced by division of existing ones
Bonus! An easy summary
| Feature | Plant | Animal | Bacteria |
| Cell wall | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Cell membrane | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Nucleus | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Cytoplasm | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Chloroplasts | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Ribosomes | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Mitochondria | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Vacuoles | ✔️ | (✔️) | ❌ |
| Circular DNA | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Plasmids | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ |
Special Cells
Specialised cells have different functions:
- Ciliated cells -> Movement of mucus in the trachea and bronchi
- Root hair cells -> Absorption
- Palisade mesophyll cells – > Photosynthesis
- Neurons -> Conduction of electrical impulses
- Red blood cells -> Transport of oxygen
- Sperm and egg cells (gametes) -> Reproduction
Levels of Organisation
Cell – Small building blocks that make up organisms
↓
Tissue – A group of similar cells working together
↓
Organ – A group of different tissues worting together to perform specific functions
↓
Organ system – Different organs that work together
↓
Organism – All the different organ systems