IGCSE Biology 0610
3.2 Osmosis
The Role of Water as a Solvent in Organisms
- Dissolved substances easily transported
- Digested food molecules moved to cells
- Toxic substances and excess salts dissolve in water and urinated out
- 75% of cytoplasm and most chemical reactions in cells are in water
Osmosis
- Osmosis is the net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential (dilute solution) to a region of lower water potential (concentrated solution), through a partially permeable membrane
- Water diffuses through partially permeable membranes by osmosis
- Water moves into and out of cells by osmosis through the cell membrane
Bonus! Identifying higher and lower water potential
Think of higher water potential as having a higher concentration of water molecules. Water itself would obviously have lots and lots of water molecules. But if you were to mix some salt or sugar into the water, the concentration of water molecules would become lesser and therefore have a lower water potential than just water. So the more solute is added to the water, the lower the water potential would be.
Investigating Osmosis
Dialysis Tubing:
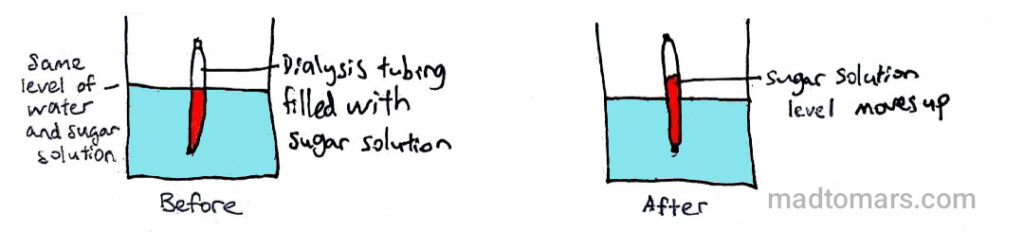
Why?
The water is a dilute solution with high water potential. The sugar solution is a concentrated solution with low water potential. Water molecules diffuse through the dialysis tubing, which is partially permeable, to the sugar solution through osmosis.
Osmosis in Plant Tissues:
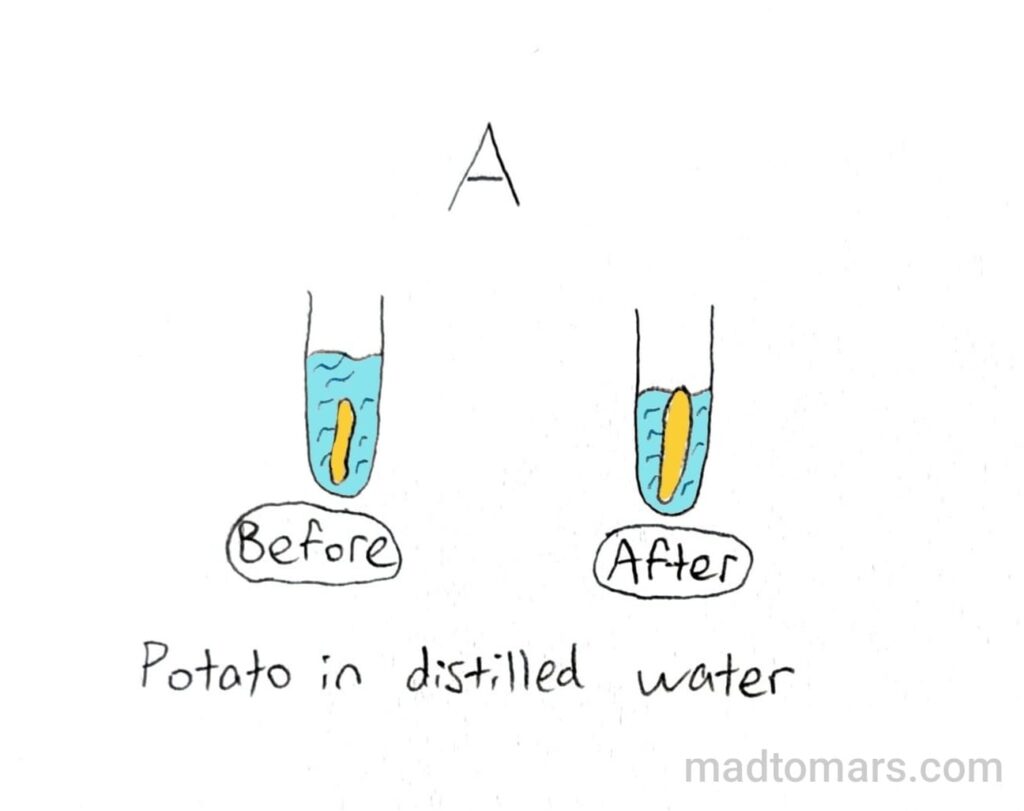
↓
Cell swells as water pushes against cell walls creating turgor pressure
↓
Cell contains as much water it can hold
↓
Cell wall stops it from bursting
↓
Cell is turgid
Turgid cells give plants support
(potato becomes longer)

↓
No water potential gradient, no diffusion of water in or out
↓
No change
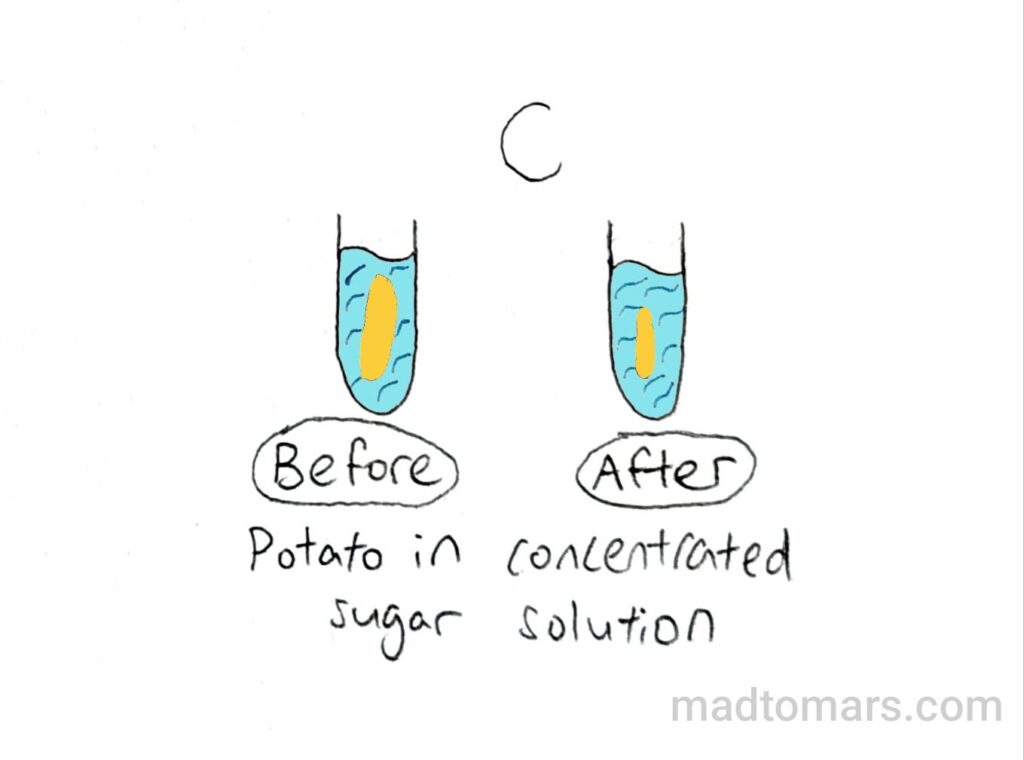
↓
Sap vacuole shrinks
↓
Cells become flaccid
↓
Cytoplasm moves away away from cell wall
↓
Cells are plasmolysed
(potato becomes shorter)
Importance of Water Potential and Osmosis for Organisms
Plants
- Plants need osmosis to maintain cells being turgid
- Plant cells become flaccid if they lose too much water
- Plants are supported by the pressure of water inside the cells pressing outwards on the cell wall
Animals
- If too much water diffuses out of animal cells, they shrink
- If too much water diffuses into animal cells, they burst as there is not cell wall